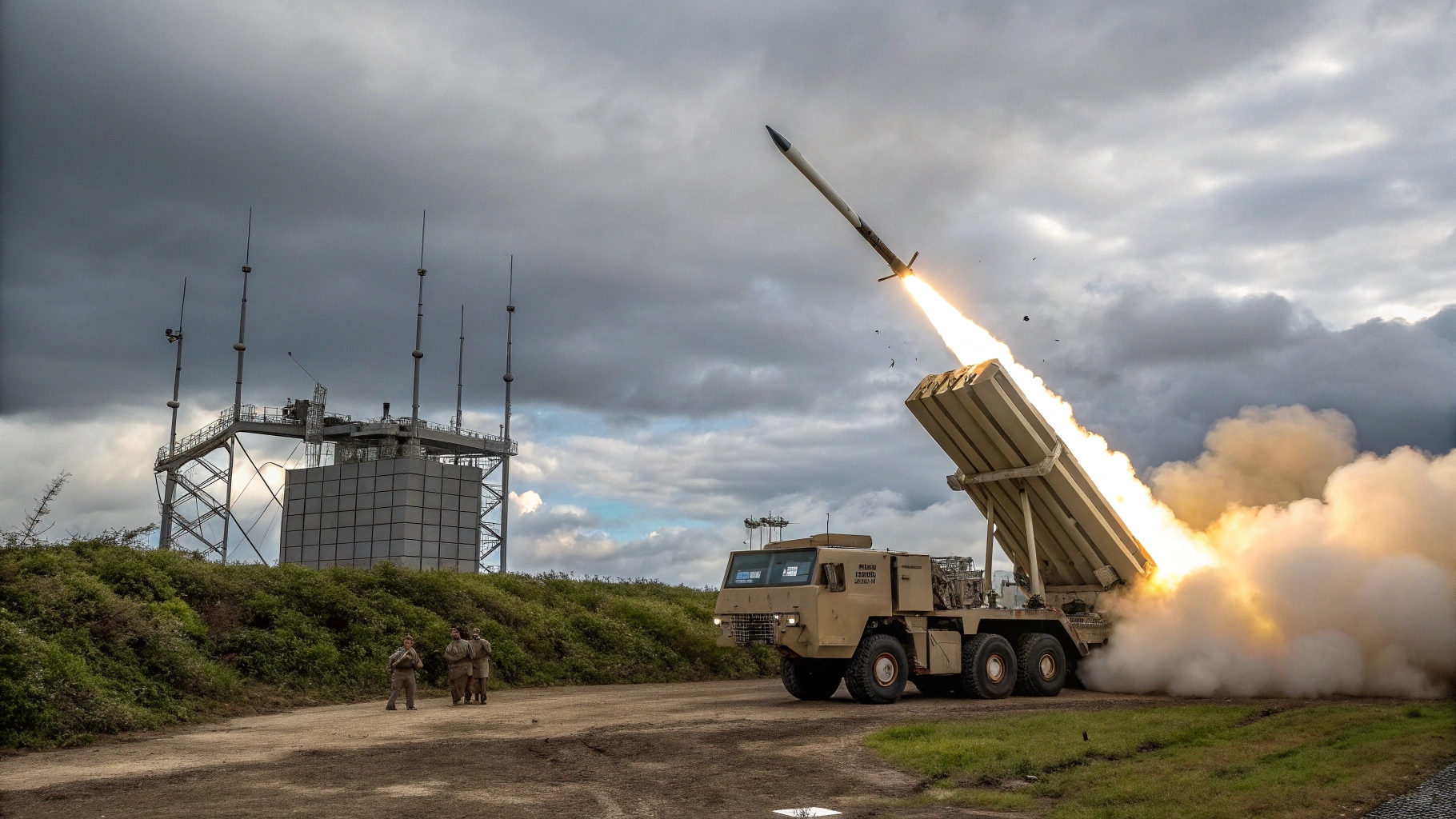
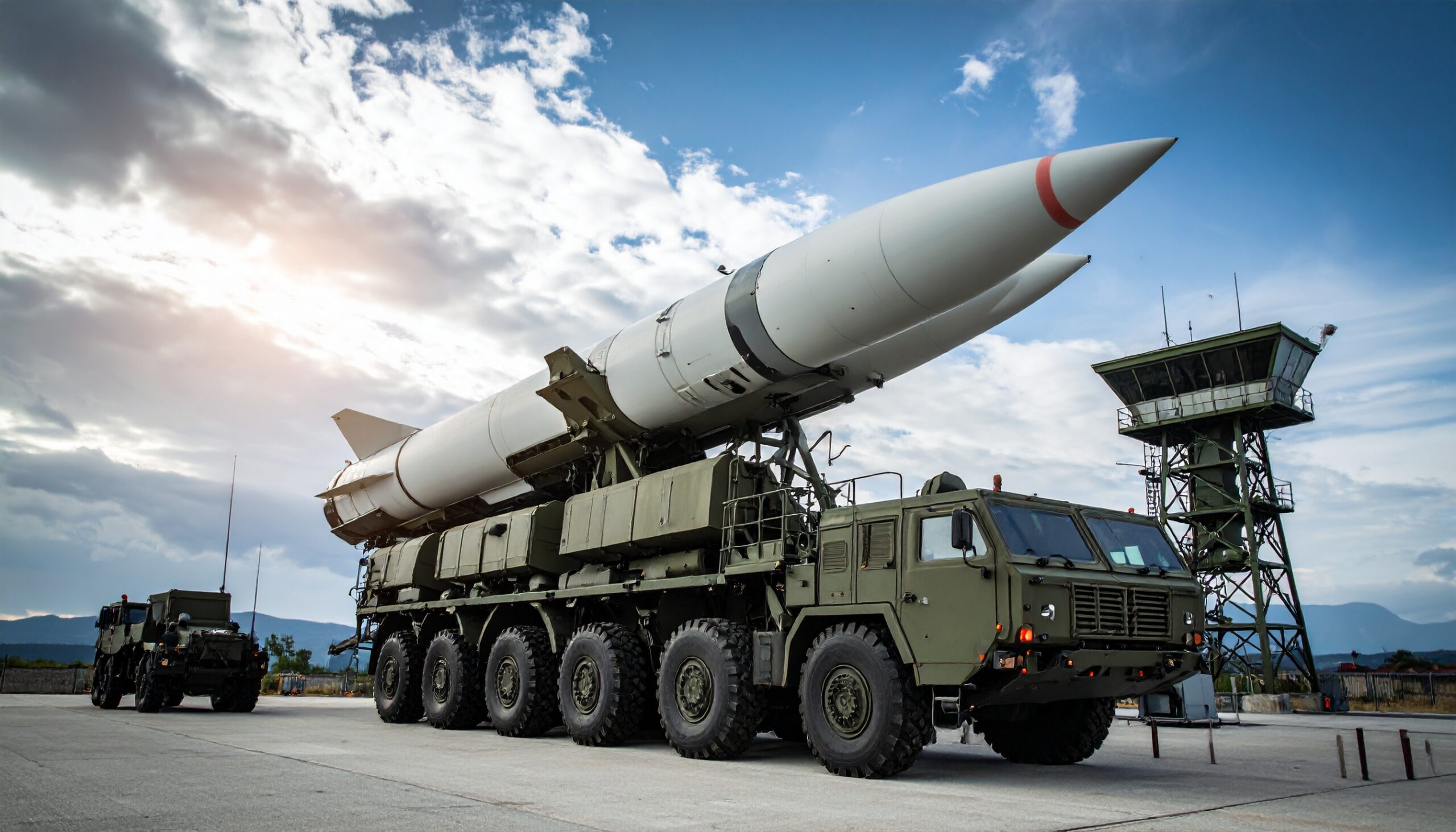
Norway has selected South Korea’s K239 Chunmoo multiple launch rocket system (MLRS) from Hanwha Aerospace, opting for the Korean platform over rival offerings from European and US defense firms. Announced by the Norwegian government, the decision includes the procurement of 16 Chunmoo launchers along with a substantial stock of missiles spanning three range categories, including long-range strike weapons capable of reaching up to 500 kilometers.
According to the announced timeline, launcher deliveries and training equipment will take place in 2028 and 2029, followed by missile deliveries in 2030 and 2031. The program represents one of the largest modernization investments in Norwegian Army history and marks a significant shift away from Norway’s traditionally Europe- and US-centric defense procurement strategy.
The Chunmoo selection builds on Norway’s existing defense cooperation with South Korea, following the earlier acquisition of K9 Vidar self-propelled howitzers from Hanwha. In November 2025, Oslo narrowed its rocket artillery competition to Chunmoo and Lockheed Martin’s HIMARS, eliminating the EuroPULS system proposed by Elbit Systems and KNDS Deutschland.
Missile range and flexibility were decisive factors in the evaluation. The Chunmoo can deploy multiple missile types, including long-range variants that exceed the reach of competing commercial systems. Norwegian officials also cited faster delivery timelines and lower overall costs as key advantages. Hanwha’s expanding European supply chain centered in Poland, where nearly 300 Chunmoo systems are being acquired and missiles will be produced locally, further strengthened the bid.
In addition, Hanwha proposed an industrial cooperation package worth 120 percent of the contract value, involving Norwegian companies, and agreed to receive payment only after deliveries begin. With this acquisition, Norway joins a growing number of NATO allies adopting the Chunmoo system, adding a powerful long-range strike capability to NATO’s northern flank amid increasing regional security challenges.